Using OPUS to compute a precise point with the EMLID Reach RS2 +
Using OPUS to get an accurate point from your base station
If possible, use the ROCK RTK Network instead: https://learn.rockrobotic.com/rocknet
NOAA's Online Positioning User Service (OPUS)
Online Positioning User Service (OPUS) is provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). With OPUS you may accurately determine the coordinates of a static point anywhere on the territory of the United States without real-time corrections or a base station nearby.
In this guide, we will walk you through the following steps:
- Recording RINEX data on the Emlid Reach.
- Exporting raw data from the Emlid Flow to your mobile device.
- Uploading the collected file to OPUS.
- Entering the obtained base coordinates into PCMaster and ROCK Cloud.
The equipment you need to accomplish the survey:
- Emlid Reach receiver
- Tripod
How OPUS works:
A receiver in a standalone positioning mode finds out its position relying on the data obtained from satellites only. Along with raw data, it also gets navigation messages containing such data as satellite clock offset, the ionospheric and tropospheric corrections, etc. When the corrections from the base are received, these offsets are eliminated as both receivers work in the same conditions.
OPUS allows the single receiver to achieve high-level accuracy without the use of corrections from the base station. To calculate the coordinates, OPUS uses corrections from the National Spatial Reference System (NSRS). OPUS works with software that uses data from the NOAA CORS Network for computations. This network of Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) provides Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data consisting of carrier phase and code range measurements in support of three dimensional positioning, meteorology, space weather, and geophysical applications.
Thereby, the Single receiver might determine its position with a centimeter-level accuracy using only its own raw data and precise ephemerides and clock offsets provided by a NSRS.
The coordinates are the average of three independent, single-baseline solutions, each computed by double-differenced carrier-phase measurements from one of three nearby CORSs.
NOAA's OPUS service overview
OPUS service uses dual-frequency GPS data for solution computation and supports the Static mode only. The Static data is required to be recorded on the stationary unmoving receiver.
There are 2 ways you can process the data in OPUS:
- Static (for data that are 2 to 48 hours in duration)
- Rapid-Static (for data that are 15 minutes to 2 hours in duration)
The Static and Rapid-Static methods use different processing software and provide pretty similar horizontal accuracy. The Rapid-Static processing has more strict requirements for the data quality in comparison with the Static approach. Moreover, Rapid-Static processing is available only for some regions.
NOTE
In this guide, we will show you how to process raw data from Reach RS2 using the Static method.
You can learn more about NOAA's OPUS service on their official site.
Placing Reach
Place an Emlid Reach device precisely above the marked point on the tripod and level it. Learn more about placing the Reach receiver in this guide.
Recording RINEX data on Reach
- Go to the the GNSS settings tab.
- Choose Static Positioning mode, enable BDS, GAL, GLO, GPS, and QZS only and set up the update rate to 1 Hz.
- Navigate to the Logging tab.
- Select RINEX 3.XX Raw data format (Latest).
- Enable raw data logging and record the data for 2.5 hours at least.
TIP
You may log the data from 2 hours to 24 hours depending on the accuracy required.
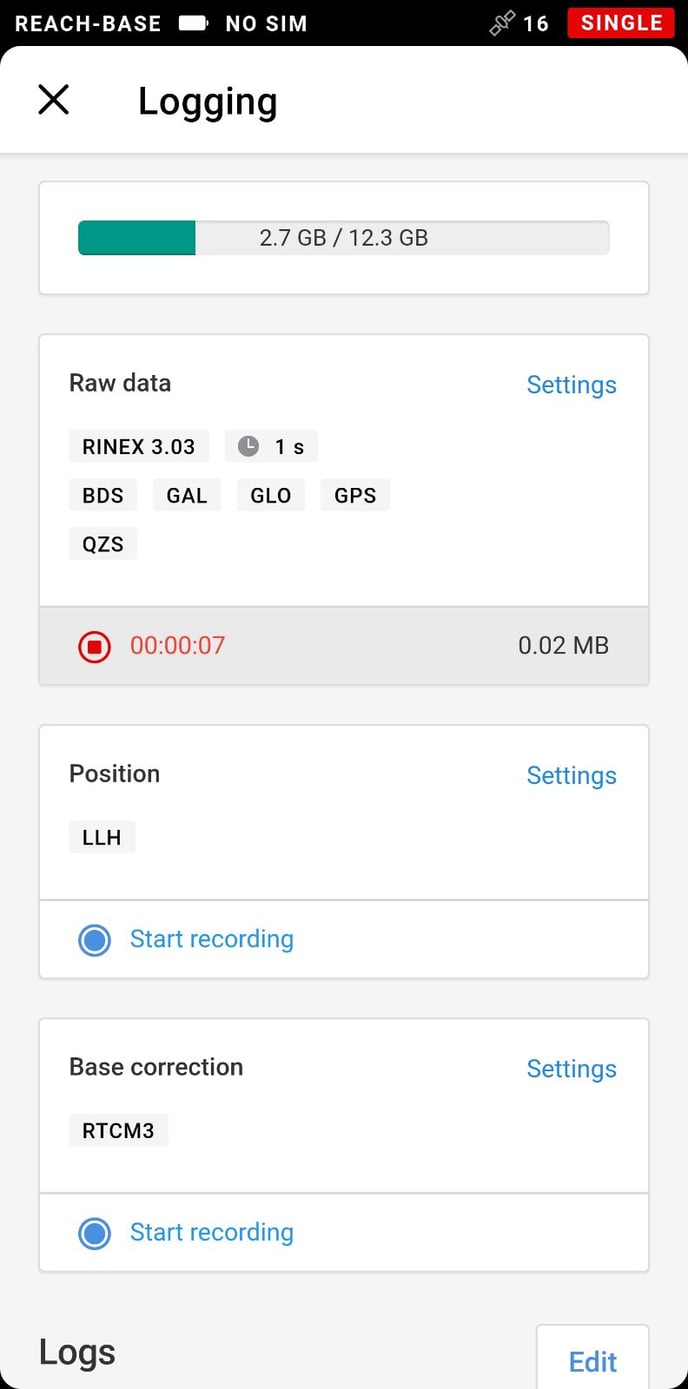
- Once you finish the survey, don't forget to toggle off raw data recording in the Logging tab.
Exporting raw data from Emlid Flow
After you finish raw data logging, you may download RINEX data from Reach to your mobile device.
- In Emlid Flow, go to the Logging tab.
- Tap on the Download button to export the RINEX file (note: You don't need the UBX or any others for that matter).
Submitting data to NOAA's OPUS service
- Go to the NOAA's OPUS site.
- Click on the Choose file button and browse for raw*.obs or .25o file you would like to process (note: you might need to rename it for OPUS)
- If you work with Reach RS2, choose the EML_REACH_RS2 NONE in the Antenna field.
- Type a pole height in the Antenna Height box.
- Enter your email address to get the results.
- Click on Upload to Static button to submit the data.
OPUS will send the file with the solution to your email address.
Results assessment
After you get the solution report, it might be useful to check how accurate the results are.
In the solution report, you will get the name of the used reference frame, the XYZ and LLH coordinates of the point and accuracy estimation in meters. Additionally, you can check these fields: OBS USED, FIXED AMB, OVERALL RMS.
The most accurate OPUS solutions have the following characteristics:
- Over 90% of observations are used,
- Over 50% of ambiguities are fixed, and
- Overall RMS is less than 3 cm.
Taking the Results
Here is an example OPUS solution:

In this report we have 93% of Observations used, 77% Fixed and an overall RMS of 0.019(m) This looks good!
Now let's look at the 3 boxed numbers, we have the LAT, W LON, and EL HGT. These are the 3 values you will use in PCMaster.
If you entered an antenna height in the OPUS screen then the The EL Height (Ellipsoid) will be of the point on the ground. For PCMaster, we want the point of the phase center of the Reach RS2. To get this, you will add your antennea height + the EMLID height of 0.134 to EL Height. So, In this case that would be 247.252+2.00(pole height) + 0.134 = 249.386
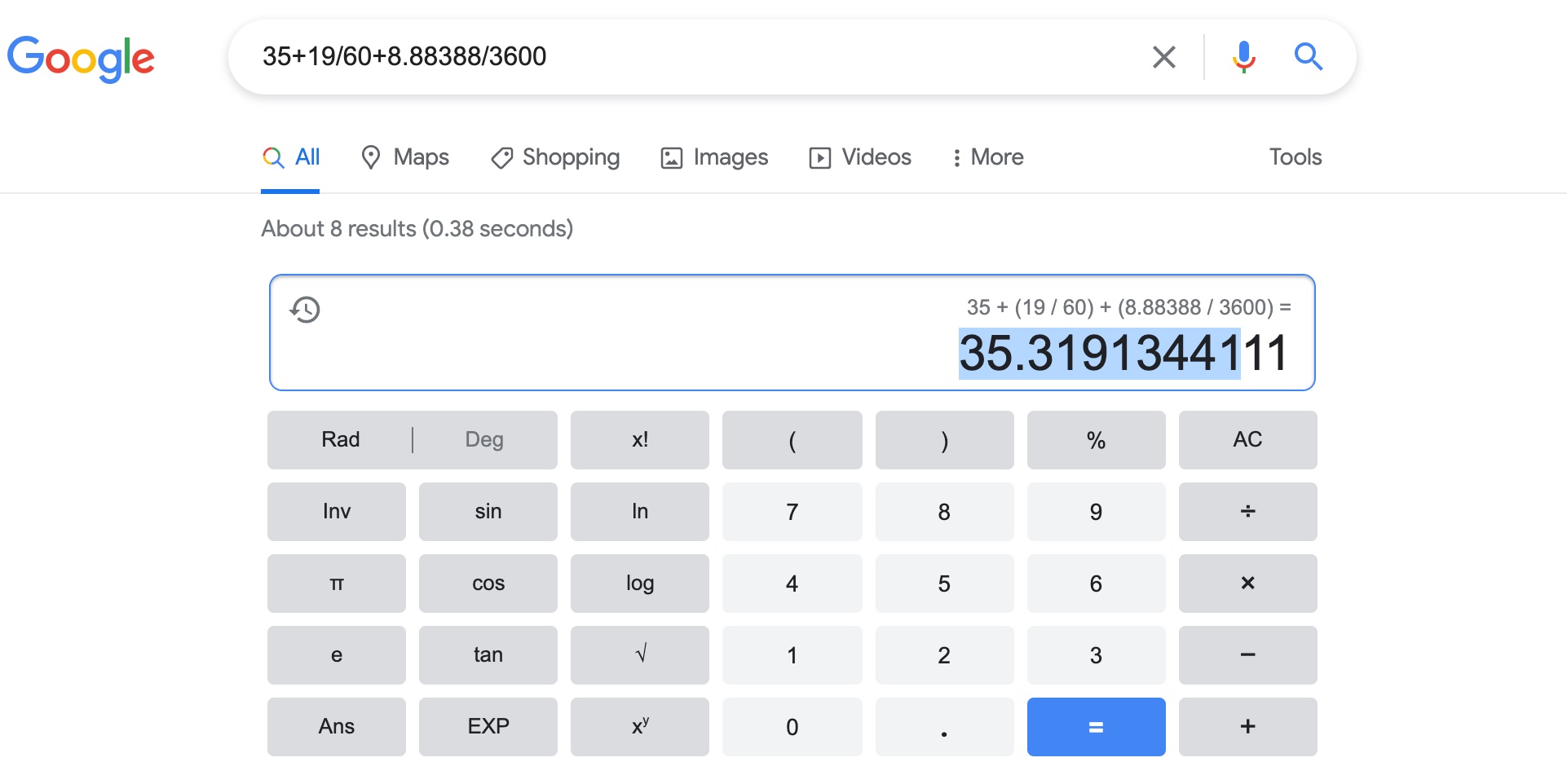
Convert the LAT and LONG from degree min second to decimal degrees
You need to get the degree min seconds format into decimal degrees.
to do this, use this formula in excel:
decimal degrees = D + M/60 + S/3600
where D = degree = 35
M = minute = 19
S = second = 8.88388
Warning: W LON is always a negative value. Keep this in mind!
If you have converted correctly, you will get:
LAT = 35.3191344
LON = -96.45775378
EL Height =249.386
![ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png]](https://learn.rockrobotic.com/hs-fs/hubfs/ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png?width=250&height=50&name=ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png)