Photogrammetry vs. LiDAR: Which is Best for Your Project?
Both photogrammetry and LiDAR are useful technologies for surveying projects. The choice of which one to use depends on your specific project requirements.
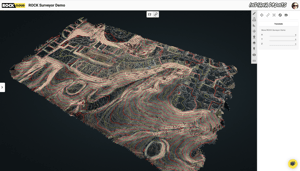 When it comes to surveying projects, two popular technologies that are used to gather data are photogrammetry and LiDAR. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages; the choice of technology depends on the specific project requirements. This article will compare photogrammetry and LiDAR and discuss when it is best to use one over the other.
When it comes to surveying projects, two popular technologies that are used to gather data are photogrammetry and LiDAR. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages; the choice of technology depends on the specific project requirements. This article will compare photogrammetry and LiDAR and discuss when it is best to use one over the other.
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is the science of measuring and interpreting imagery taken from cameras. It involves using photographs to create maps, digital terrain models, and 3D models. Photogrammetry software is used to process the images and extract the required information. The software can extract coordinates, elevations, and other information from the images.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a technology that uses laser beams to map the environment. LiDAR sensors emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for the pulse to travel to the target and back. The sensor then uses this information to calculate the distance to the target. LiDAR can be used to create detailed 3D maps and digital terrain models.
Advantages of Photogrammetry
One of the main advantages of photogrammetry is that it is less expensive than LiDAR. Photogrammetry requires less specialized equipment and can be done with a standard camera. Additionally, photogrammetry can extract detailed information from images, such as textures and colors.
If you want to learn more about ROCK's photogrammetry offerings, please review our FAQ article.
Advantages of LiDAR
LiDAR would be a better choice than photogrammetry methods for an aerial land surveying project in specific scenarios, especially when the project requires high accuracy and detailed information. Some specific reasons to use LiDAR over photogrammetry methods in an aerial land surveying project include:
- LiDAR can penetrate vegetation and map the ground beneath, making it ideal for mapping areas with dense vegetation such as forests, where photogrammetry methods would have difficulty capturing the information.
- LiDAR has a higher point density than photogrammetry, which means it can create more detailed maps and digital terrain models. This is particularly important when the project requires high accuracy and detailed information of the terrain.
- LiDAR can be used to gather data at night and in poor visibility conditions, making it useful for emergency and search and rescue operations where time is critical and visibility is limited.
- LiDAR can provide accurate measurements of the elevation, slope, and roughness of the terrain, which is useful for infrastructure planning and environmental monitoring. Photogrammetry methods may not be able to provide such detailed information.
- LiDAR can detect small and hard-to-see features, such as utility poles, power lines, and other man-made structures, that are difficult to detect with photogrammetry.
- LiDAR can capture a large amount of data quickly, making it suitable for large-scale mapping projects where time and coverage are critical.
Both photogrammetry and LiDAR are useful technologies for surveying projects. The choice of which one to use depends on your specific project requirements.
Visit rockrobotic.com to learn more about ROCK Robotic's survey-grade LiDAR hardware and software.
![ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png]](https://learn.rockrobotic.com/hs-fs/hubfs/ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png?width=250&height=50&name=ROCK-robotic-community-logo.png)